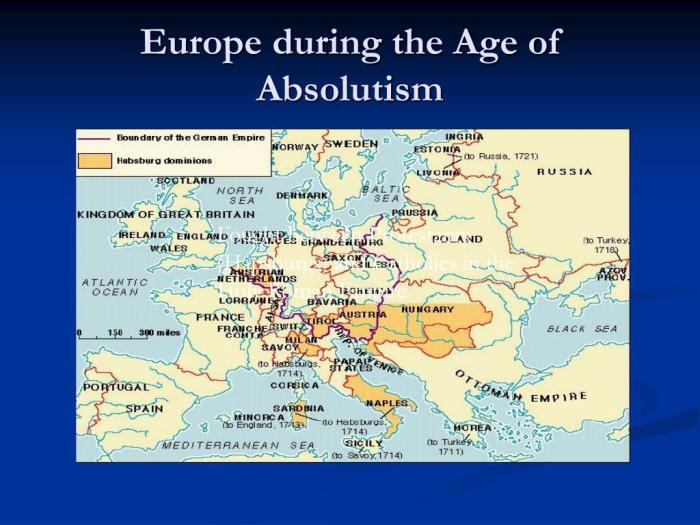
Geography of the age of absolutism in europe map – Embark on a captivating journey through the geography of the Age of Absolutism in Europe. This era witnessed the rise of absolute monarchies, shaping the political, social, and economic landscape of the continent. Delve into the intricacies of territorial expansion, trade networks, religious influences, and the profound impact of colonialism.
From the shifting boundaries of European nations to the flourishing of major trade routes, this comprehensive exploration unravels the intricate tapestry of the Age of Absolutism. Discover how absolute monarchs leveraged natural resources, improved infrastructure, and fostered urbanization to consolidate their power and transform the face of Europe.
Absolute Monarchies in Europe
During the Age of Absolutism, several European nations adopted absolute monarchies, characterized by the concentration of supreme power in the hands of a single ruler. The following table lists the countries that were absolute monarchies during this period, along with their start and end dates:
| Country | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|
| France | 1643 | 1789 |
| Spain | 1516 | 1868 |
| Austria | 1683 | 1918 |
| Prussia | 1701 | 1918 |
| Russia | 1682 | 1917 |
Geographical Boundaries and Territorial Expansion: Geography Of The Age Of Absolutism In Europe Map
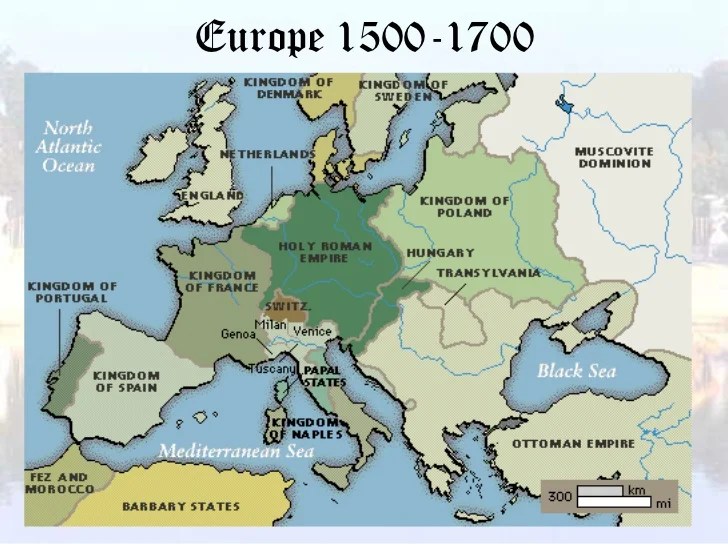
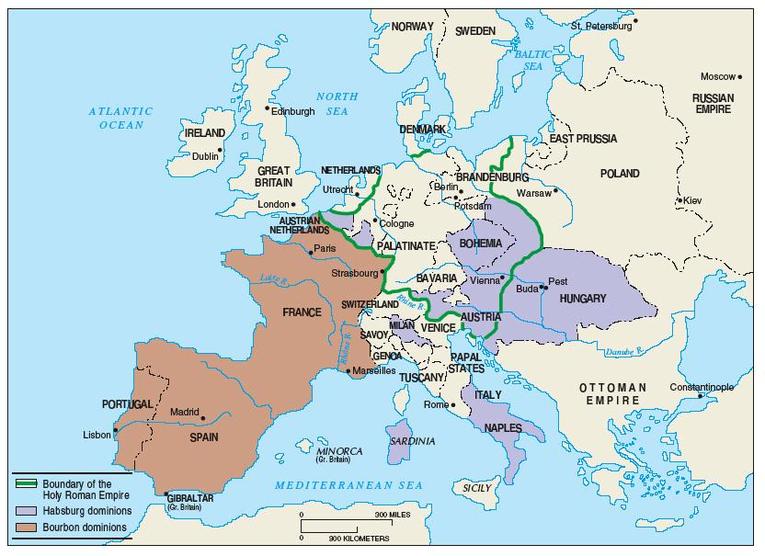
The geographical boundaries of Europe during the Age of Absolutism were largely defined by the major mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines. The Pyrenees Mountains separated France from Spain, while the Alps formed a natural barrier between Italy and the rest of Europe.
The Rhine and Danube rivers were important trade routes and played a significant role in shaping the political landscape of the continent. Over time, the boundaries of Europe expanded through territorial conquests and colonization.
Trade and Commerce, Geography of the age of absolutism in europe map
Trade and commerce played a vital role in the Age of Absolutism. Absolute monarchs used trade to strengthen their power by controlling access to valuable resources and by levying taxes on goods. Major trade routes included the Silk Road, the Spice Route, and the Atlantic trade routes.
Commercial centers such as London, Amsterdam, and Venice became wealthy and influential during this period.
- Benefits of trade for absolute monarchs:Increased revenue, access to resources, strengthened alliances
- Challenges of trade for absolute monarchs:Competition from other nations, piracy, economic crises
Religious and Cultural Influences
Religion played a significant role in the geography of the Age of Absolutism. The Protestant Reformation and the subsequent religious wars divided Europe along religious lines. The Catholic Church and the various Protestant denominations competed for influence and power, and their beliefs shaped the political and social landscape of the continent.
Religious conflicts impacted territorial boundaries and trade routes.
Natural Resources and Economic Development
Natural resources were essential for economic development during the Age of Absolutism. Absolute monarchs used natural resources such as timber, minerals, and agricultural land to support their economies. The discovery of new resources, such as gold and silver in the Americas, led to increased wealth and economic growth.
- Ways absolute monarchs used natural resources:Funding wars, building infrastructure, supporting industry
Transportation and Infrastructure
The state of transportation and infrastructure in Europe during the Age of Absolutism was generally poor. Roads were often unpaved and difficult to travel, and bridges were scarce. Absolute monarchs improved transportation and infrastructure to facilitate trade and communication. They built new roads, canals, and bridges, which made it easier to transport goods and people.
These improvements contributed to the rise of absolutism by strengthening the power of the central government.
“The construction of the Canal du Midi in France, completed in 1681, was a major engineering feat that connected the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea. It significantly improved trade and communication, and helped to strengthen the French monarchy.”
Urbanization and Population Growth
The Age of Absolutism witnessed significant urbanization and population growth. Absolute monarchs encouraged urbanization by granting privileges to cities and by promoting economic development. The growth of cities led to increased trade, commerce, and cultural exchange. By 1700, London had become the largest city in Europe, with a population of over 500,000.
- Factors contributing to urbanization and population growth:Improved sanitation, increased economic opportunities, migration from rural areas
Colonialism and Imperialism
Colonialism and imperialism played a significant role in the Age of Absolutism. Absolute monarchs used colonialism and imperialism to expand their power and wealth. European nations established colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, and they exploited the resources of these colonies to support their economies.
Colonialism and imperialism led to increased trade, wealth, and global influence for European nations.
FAQ Insights
What were the major trade routes during the Age of Absolutism?
The major trade routes included the Baltic Sea trade route, the Mediterranean Sea trade route, and the Atlantic trade route.
How did absolute monarchs use natural resources to support their economies?
Absolute monarchs used natural resources to fund their armies, build palaces, and support their lavish lifestyles.
What were the factors that contributed to urbanization and population growth during the Age of Absolutism?
Factors that contributed to urbanization and population growth included improved agricultural techniques, increased trade, and the rise of manufacturing.